How Ad Servers Work
Written by Roy
6 min read
1. What is an ad server? 2. How does an ad server work? 3. What are ad servers used for? 4. Benefits of ad servers 5. Ad servers vs. ad networks 6. Examples of ad servers 7. Conclusion What is an ad server?An ad server is a platform used to manage and deliver online ads on publisher's websites and apps. Ad servers play an important role in digital advertising as it automates the process of ad placement across websites, while ensuring that ads are served to the right user at the right time. There are two types of ad servers: first-party ad servers and third-party ad servers. Let's break that down first. First-party ad serversFirst-party ad servers are also called publisher ad servers and they are one of the first to be called when a user opens a web page. Publisher use them to manage and deliver ads directly on their own websites or apps. A first-party ad server has features to optimize ad inventory, control what type of ads are displayed and ensure a quality ad experience by using ad targeting and frequency capping. Third-party ad serversThird-party ad servers are used by advertisers and therefore also called advertiser ad servers. Their goal is to deliver ads across multiple publishers, while tracking performance and optimizing campaigns in an automated way. Ad servers for advertisers have features that are different from those you'll find in a publisher ad server. Here's an overview of the main differences between first-party ad servers and third-party ad servers. 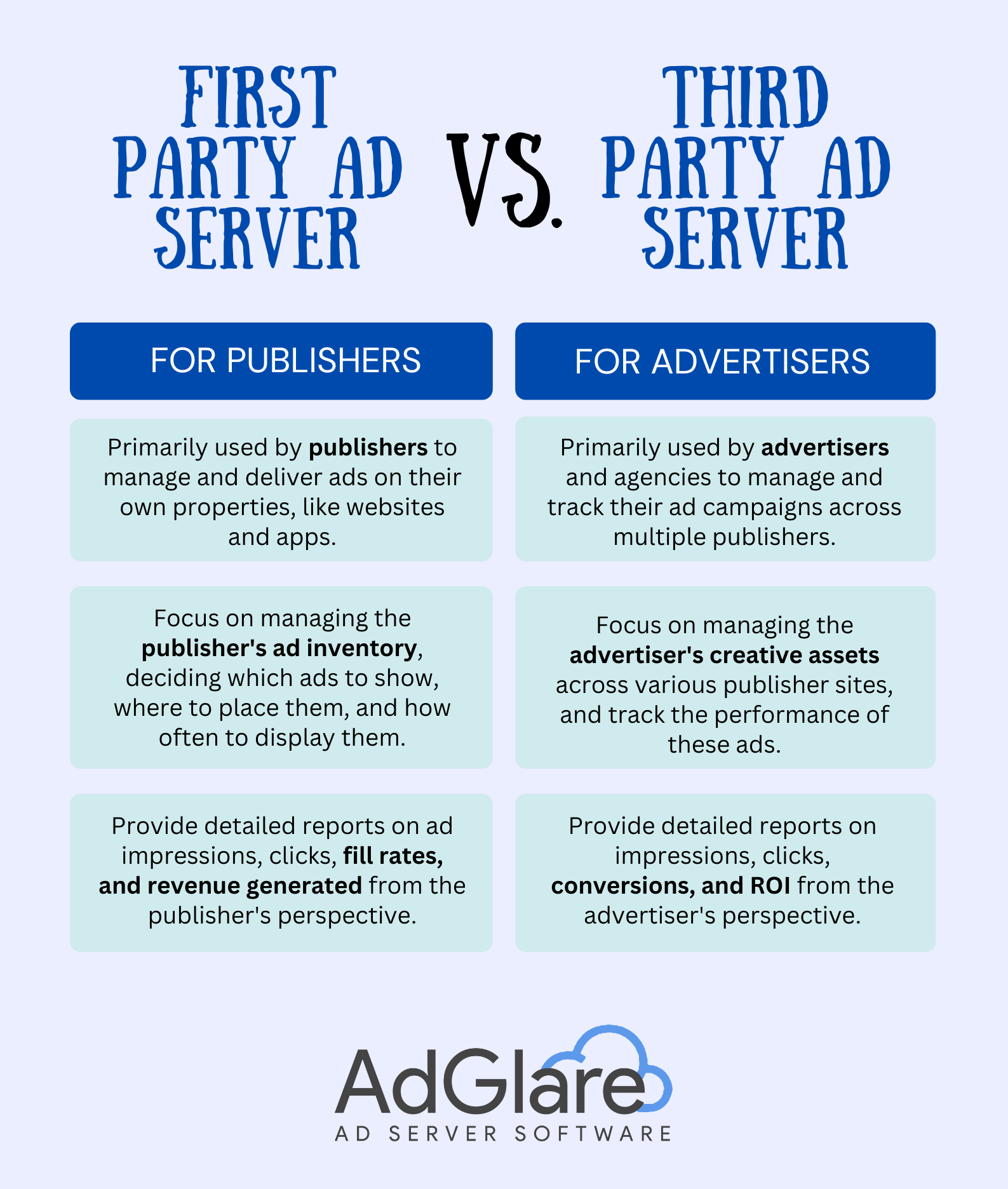 Download this infographic here:
How does an ad server work?Ad servers, like AdGlare, work through a series of steps to deliver the right ads to the user. This generally happens in less than a few milliseconds. Let's see how that works in more detail for a publisher ad server:
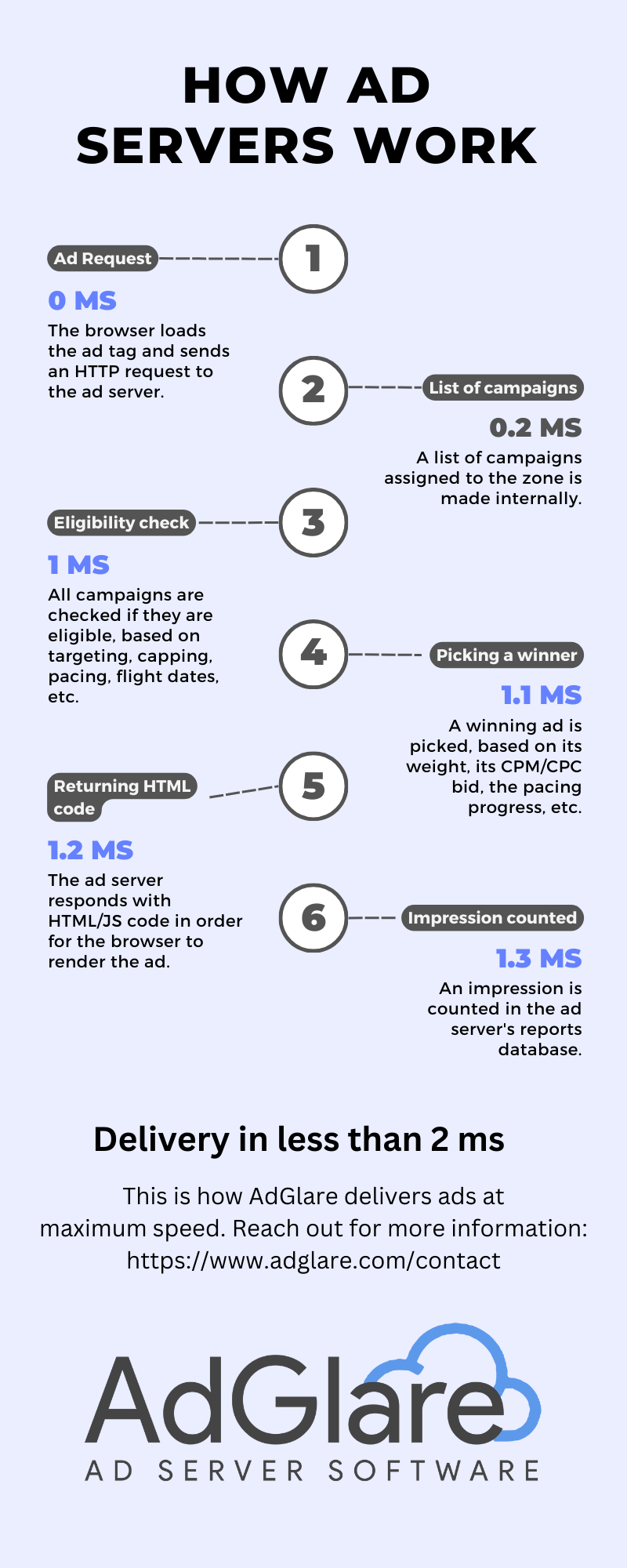 Download this infographic here:
But what if a third-party ad server is involved?When an advertiser ad server is involved, the workflow includes additional steps between step #5 and #6. Instead of returning the code that makes up the ad, the publisher's ad server invokes the advertiser's ad server via a second ad tag. The advertiser's ad tag is then executed by the browser and the third-party ad server responds with the actual HTML/JS code that creates the ad. Including a third-party ad server allows for both parties (publishers and advertisers) to track key metrics at the same time. Advertisers can then compare report numbers with the ones provided by publishers, before paying the publisher for the campaign. While comparing reports, ad discrepancies are usally a source of debate. What are ad servers used for?Ad servers have various roles and important features, for both parties in the digital advertising ecosystem. Depending on whether you're a publisher or an advertiser, here are some common reasons why ad servers are used:
Benefits of ad serversAd servers are a key element in the online advertisement ecosystem. Although, in theory, we could do without, ad servers have benefits for both publishers and advertisers. Ad servers help publishers by managing ad inventory (ad spots), while increasing ad revenue by serving the most relevant or highest paying ads first. Publishers have full control over which ad is displayed when and where. For advertisers, ad servers are important to optimize campaigns by providing reports with key metrics like CTR and conversion rates. If a campaign is not doing well, advertisers can change the creatives on the fly without the need to contact the publisher. Ad servers vs. ad networksToo often we get the question if AdGlare provide ads to publishers. Let me therefore briefly explain the difference between ad servers and ad networks. While both are important components in the ad tech industry, they serve a completely different purpose and have different functions. An ad server stores creatives, select the best ad and provides reports on ad performance. It focuses on the technical aspect of getting the ad in front of the user. Ad servers are used by publishers to serve campaigns made from direct deals with advertisers. Ad networks, on the other hand, are marketplaces that act as a middleman between advertisers and publishers. By aggregating ad inventory from multiple publishers, they offer a variety of ad placements to advertisers. Ad networks simplify the process for advertisers to find inventory, while at the same time offering a one-stop solution to publishers to monetize their content. Ad networks generally use ad servers to manage inventory and serve campaigns. Examples of ad serversAre you looking for an ad server? In this section, I will outline some of the most prominent players in the ad tech industry. Here are some ad server examples:
List of ad serversThere's also an interactive list of ad servers, where you can compare features, requirements, costs and more.ConclusionAn ad server is a platform that manages and delivers online ads, making sure they reach the right user at the right time. There are two types: first-party ad servers, used by publishers to manage ads on their properties (website, app) and third-party ad servers used by advertisers to distribute ads across multiple websites while tracking performance. Ad servers handle tasks like campaign eligibility checking, ad selection, creative optimization and performance tracking. They play an important role in the digital advertising ecosystem ever since the first ad campaign was launched. Examples of ad servers include AdGlare, Google Ad Manager, Sizmek, Smart AdServer and OpenX. •••
About AdGlareAs an established ad server, AdGlare has over 12 years of experience in managing, serving and optimizing ads. Reach out to see how AdGlare can help you achieving your advertising goals. Or sign up for a free 14-day trial to take a quick look inside. Download this article as PDF?
No time to read the whole article? Download a free PDF version for later (no email required): Permalink
To link to this article, please use: |